MQTT - Publishing and Subscribing
TagoIO MQTT Broker is available exclusively for Starter and Scale accounts in the US database region. European (EU) database region accounts cannot access this service due to new security requirements, but they may use third‑party MQTT services with TagoIO via the MQTT Relay feature. Free accounts can access MQTT functionality through the MQTT Relay as well.
For EU accounts, a public MQTT broker without SLA guarantees is planned for the future. The main purpose of that broker will be proof‑of‑concept testing.
You can publish to your MQTT topics by coding a script that runs from an Analysis. When the Analysis runs, your script can publish a topic that will be received by any device subscribed to that specific topic. An Analysis can be started in different ways: by timer, by an Action, or by another Analysis. The diagram below illustrates the data flow from an Analysis to the MQTT network.
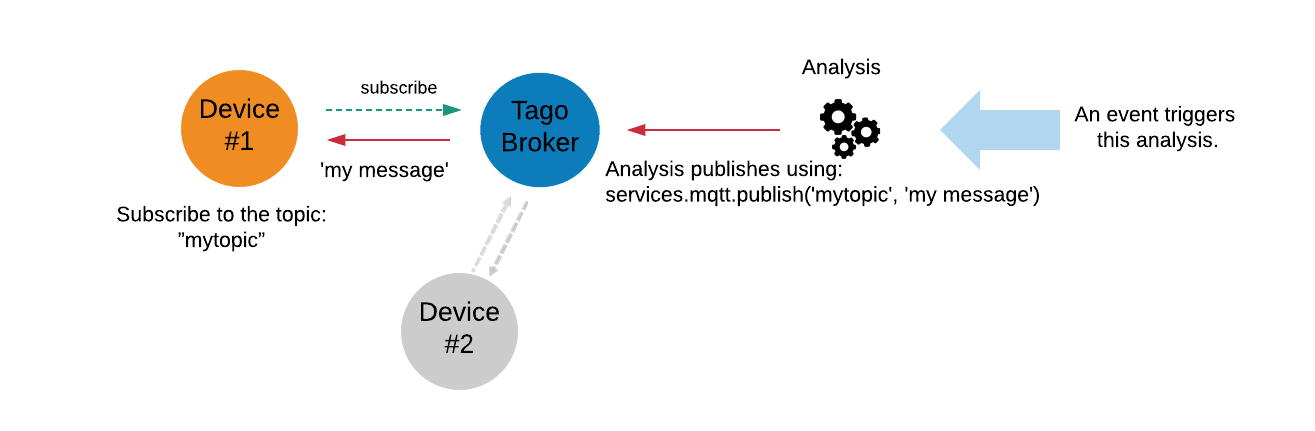
The diagram shows:
- An Analysis publishes to the broker using, for example:
// Example: publish from an Analysis
services.mqtt.publish('mytopic', 'my message')
- Any device that subscribes to the topic "mytopic" will receive the published message.
- Typical subscribe text: Subscribe to the topic: "mytopic"
This section describes how to publish and subscribe to topics on the TagoIO MQTT Broker. It assumes you already know how to connect to MQTT; if you do not, see the MQTT article for connection instructions.
Publishing to TagoIO
You can create an Action and attach it to any specific topic or wildcard topics, then trigger actions from there.
The payload can be sent directly to your bucket, trigger an Analysis, or be delivered via SMS or E‑mail.
If you send the payload in JSON format, the TagoIO backend automatically adds a metadata field with a child field called topic.
For raw payloads, transform your data into the TagoIO JSON format by wrapping it in a variable named payload and placing the raw data under value; this will also add the same metadata.topic field.
QoS and Retained Message Support
The Quality of Service (QoS) level is an agreement between the sender of a message and the receiver. TagoIO officially supports QoS 0 and 1.
TagoIO does not support the native retain feature found in standard MQTT protocol implementations; however, we offer a workaround to achieve similar functionality. Read more here: MQTT Retain on TagoIO Broker.
How to Debug MQTT with TagoIO
You can view all your connections directly on the Live Inspector and inspect any connection, payload, QoS, Last Will messages, and more.
The following actions trigger messages in the inspector:
- a client connects to the broker
- a client disconnects from the broker
- a client subscribes to any topic
- a client unsubscribes from any topic
- a client publishes to any topic
Subscribing – Single Level
The single‑level wildcard is represented by +, which matches exactly one level of a topic.
Example: If the client subscribes to home/+/temperature, the following topics will match:
home/kitchen/temperaturehome/office/temperaturehome/livingroom/temperature
Topics that will not match include:
home/kitchenhome/kitchen/humidityhome/office/ac/temperature
Subscribing – Multi Level
The multi‑level wildcard is represented by #, which matches any number of levels.
Example: If the client subscribes to home/#, the following topics will match:
home/kitchenhome/kitchen/temperaturehome/office/ac/temperaturehome/upstairs/bedroom/ac/temperature